Understanding the Link Between Sugarcane and Diabetes
Does sugarcane cause diabetes? It’s a question many health-conscious individuals ask, especially those looking to manage or prevent high blood sugar levels. Sugarcane is a naturally sweet plant rich in vitamins and minerals. But since it’s commonly associated with sugar, there’s confusion about its impact on diabetes.
Let’s break down the truth about sugarcane, blood sugar, and diabetes.
Table of Contents
What Is Sugarcane?
A Natural Source of Sugar and Nutrients
Sugarcane is a tropical grass cultivated for its juice, which is used to produce raw sugar. It contains natural sugars (sucrose), water, fiber, and small amounts of potassium, calcium, magnesium, and iron. It’s a popular natural drink in many countries due to its hydrating and energizing properties.
However, since sugarcane is naturally sweet, it raises concerns about whether its sugar content can contribute to diabetes or worsen it.
Does Sugarcane Directly Cause Diabetes?
Sugarcane vs. Refined Sugar
No, sugarcane does not directly cause diabetes. Diabetes is primarily caused by a combination of genetic factors, insulin resistance, obesity, and a diet high in processed sugars and unhealthy fats.
The sugar in raw sugarcane is natural and less processed compared to refined sugars found in sodas, candies, and baked goods. However, it still contains a high amount of simple carbohydrates, which can spike blood sugar levels if consumed in large quantities.
Is Sugarcane Bad for Diabetics?
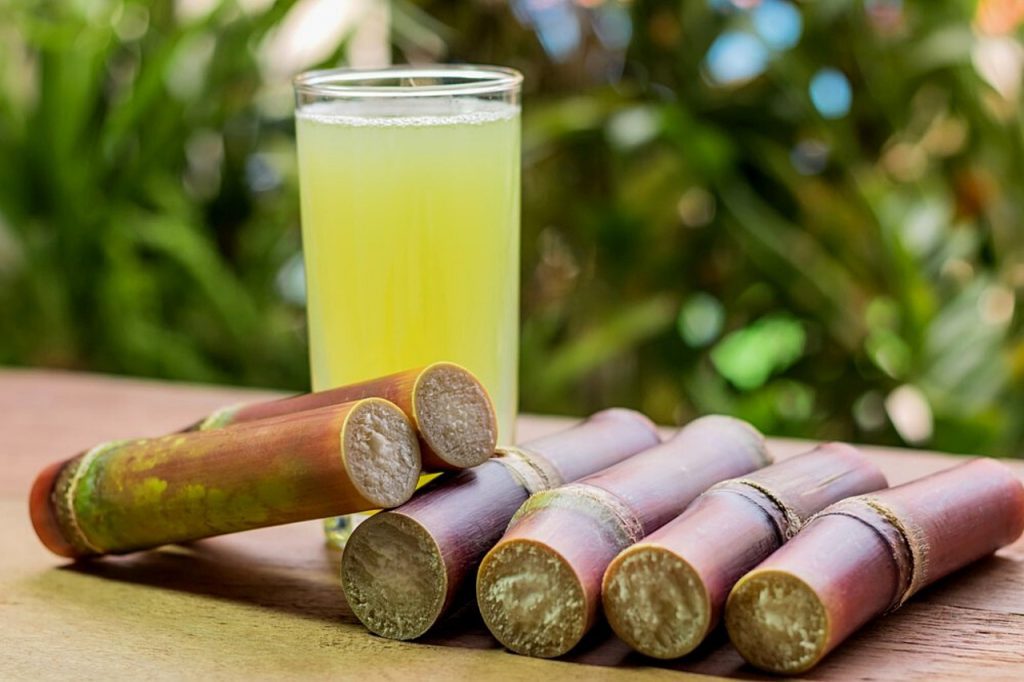

Consider the Glycemic Index (GI)
Sugarcane juice has a high glycemic index, meaning it can raise blood glucose quickly. For individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance, this can pose a problem. Despite its natural form, sugarcane juice can lead to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, especially if consumed without fiber.
So, is sugarcane bad for diabetics?
In large amounts, yes. But moderate, occasional intake under medical guidance may not be harmful for everyone.
Can Diabetics Drink Sugarcane Juice?
Moderation and Timing Matter
If you’re diabetic and wondering, can diabetics drink sugarcane juice, the answer is: yes, with caution. Here are a few considerations:
- Always check your blood sugar levels before and after drinking.
- Choose fresh juice without added sugar.
- Drink it early in the day when your body is more insulin-sensitive.
- Avoid drinking on an empty stomach.

Consult your healthcare provider before including sugarcane juice in your diet.
Natural Sugar and Diabetes: What’s the Difference?
Not all sugars are the same. While refined sugar is stripped of nutrients, natural sugars like those in fruits and sugarcane come with vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber. However, when sugarcane is juiced and the fiber is removed, it acts more like refined sugar in the body.
Key Takeaway
Natural sugar is healthier in its whole-food form. Drinking sugarcane juice without fiber makes it easier to absorb sugars quickly, leading to blood sugar spikes.
Potential Health Benefits of Sugarcane
When Consumed Responsibly
Despite the concerns, sugarcane does offer some health benefits when consumed in moderation:
- Boosts hydration: Ideal for hot climates and post-exercise recovery.
- Provides antioxidants: Helps fight oxidative stress.
- Supports liver function: Used traditionally to combat jaundice.
These benefits make sugarcane useful—but not necessarily safe for diabetics unless carefully managed.
Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Naturally
Balance Is Key
Instead of eliminating sugarcane completely, consider these blood sugar management tips:
- Increase fiber intake to slow sugar absorption.
- Exercise regularly to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Avoid sugary beverages, including sweetened sugarcane juice.
- Monitor portion sizes if including natural sugars in your diet.
For more on managing blood sugar, check out CDC’s Diabetes Management Guide.
Final Verdict: Should You Avoid Sugarcane If You’re Concerned About Diabetes?
It Depends on Your Health Status
Does sugarcane cause diabetes? Not by itself. But if consumed excessively or in processed forms, especially by individuals with prediabetes or diabetes, it can contribute to poor blood sugar control.
Sugarcane should be treated like any carbohydrate-rich food—consumed mindfully, in moderation, and preferably in whole-food form.
If you’re managing diabetes or looking to prevent it, be informed and proactive. Always read nutrition labels, consult your doctor, and choose whole, fiber-rich foods.
Stay educated. Stay healthy.
For more natural health tips and diet-friendly recipes, explore The Planttube Blog and don’t forget to check out our 35 Diabetic-Friendly Delicious Recipes.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or a qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding your health condition.








