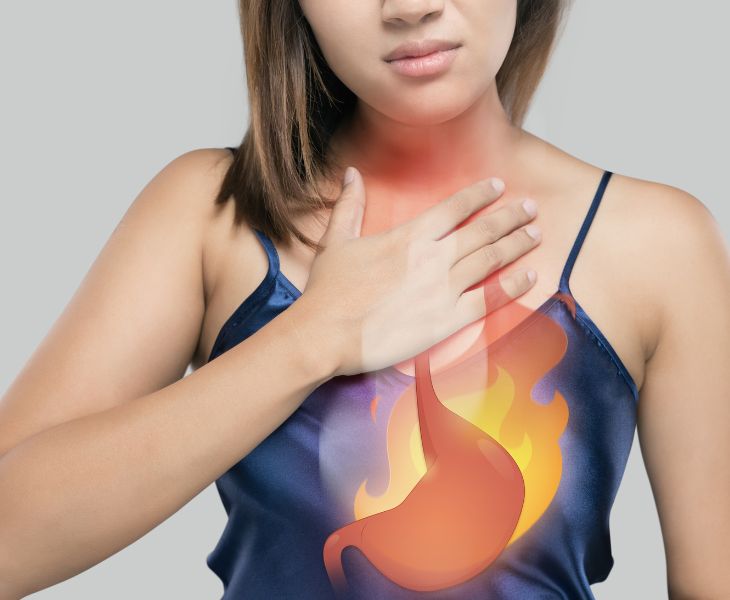
Introduction: Can Acid Reflux Be Life-Threatening?
Have you ever woken up in the middle of the night with a burning sensation in your chest or throat? You might have dismissed it as a simple case of heartburn. However, chronic acid reflux—also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)—can pose more serious risks than you might think. In rare cases, it can even be life-threatening while you sleep.
In this article, we’ll explore whether acid reflux can cause death during sleep, its potential dangers, and how you can prevent it.
Table of Contents
What Is Acid Reflux and Why Does It Happen?
Understanding Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. This happens due to a weakened or malfunctioning lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is responsible for keeping stomach acid in place.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux
Common symptoms of acid reflux include:
- Heartburn – A burning sensation in the chest.
- Regurgitation – The backflow of acid or food into the throat.
- Sore throat or hoarseness – Caused by repeated exposure to stomach acid.
- Chronic cough – Resulting from irritation in the throat.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) – Due to esophageal inflammation.
GERD: A Chronic Condition
When acid reflux becomes chronic, it is classified as GERD. If left untreated, GERD can cause severe complications, including esophageal ulcers, scarring, and even esophageal cancer.
Can You Die from Acid Reflux in Your Sleep?
The Rare but Real Danger
While it is uncommon, death from acid reflux during sleep is possible. Here’s how:
- Aspiration Pneumonia: During sleep, stomach acid can enter the lungs, causing aspiration. This may lead to pneumonia, which can be fatal if untreated.
- Choking and Suffocation: In severe cases, the regurgitation of acid or food may block the airway, leading to choking or suffocation.
- Esophageal Rupture: Although extremely rare, prolonged exposure to acid can weaken the esophagus, causing it to rupture. This is a medical emergency that can be fatal.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain individuals are more vulnerable to serious complications, including:
- People with chronic GERD
- Obese individuals (due to increased abdominal pressure)
- Pregnant women (hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach)
- Smokers and heavy drinkers
- Sleep apnea sufferers
Health Risks Associated with Nighttime Acid Reflux
1. Aspiration Pneumonia
When stomach acid or food enters the lungs during sleep, it can cause aspiration pneumonia. Symptoms include:
- Coughing and wheezing
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fever and chills
Severe cases can lead to respiratory failure, which may be fatal if not treated promptly.
2. Barrett’s Esophagus and Cancer
Chronic acid reflux can lead to Barrett’s esophagus, a condition where the esophageal lining changes. This significantly increases the risk of esophageal cancer.

3. Sleep Apnea and Acid Reflux: A Dangerous Duo
Individuals with sleep apnea are more likely to experience GERD at night. The repeated airway blockages associated with sleep apnea can increase acid reflux episodes, worsening symptoms and increasing the risk of aspiration.
How to Prevent Acid Reflux While Sleeping
1. Sleep Position Matters
Your sleeping posture can significantly impact acid reflux episodes. To reduce the risk:
- Sleep on your left side – This position reduces acid exposure in the esophagus.
- Elevate the head of your bed – Use a wedge pillow or raise the bed by 6–8 inches to prevent acid from flowing upward.

2. Avoid Eating Before Bedtime
Eating late at night can trigger reflux. It’s best to:
- Stop eating 3 hours before sleeping.
- Avoid spicy, fatty, and acidic foods before bed.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight increases abdominal pressure, making reflux worse. Losing weight can significantly reduce GERD symptoms.
4. Dietary Changes
Incorporate reflux-friendly foods into your diet, such as:
- Oatmeal – Soothes the stomach and reduces acid.
- Bananas – Naturally low in acid.
- Ginger tea – Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
5. Use Medications When Necessary
Over-the-counter and prescription medications can help manage acid reflux:
- Antacids – Neutralize stomach acid.
- H2 blockers – Reduce acid production.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) – Lower acid production more effectively.
FAQs About Acid Reflux and Sleep Safety
1. Can you choke to death from acid reflux while sleeping?
Yes, though rare, severe reflux can cause aspiration, potentially blocking the airway and leading to suffocation.
2. What are the warning signs of severe nighttime acid reflux?
- Difficulty breathing or coughing at night.
- Frequent waking due to choking or regurgitation.
- A sour taste in the mouth upon waking.
- Hoarseness or a sore throat in the morning.
3. Should I see a doctor if I have nighttime acid reflux?
Yes. Chronic or severe GERD can lead to serious complications. See a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Frequent reflux episodes (more than twice a week).
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Chest pain or breathing difficulties.
Key Takeaway: Don’t Ignore Nighttime Acid Reflux

While dying from acid reflux in your sleep is rare, it is still possible, especially for individuals with severe GERD or underlying respiratory conditions. The good news is that simple lifestyle changes and medical interventions can significantly reduce the risks.
If you experience frequent nighttime reflux, consult a doctor to prevent serious complications. Prioritize your gut health and quality sleep by making mindful dietary and lifestyle choices.
Take control of your acid reflux today! For more health tips, natural remedies, and wellness guides, visit ThePlantTube for expert insights and practical advice.
Authoritative References
- American Gastroenterological Association – GERD guidelines and prevention tips.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – Acid reflux and GERD resources.
- Cleveland Clinic – Sleep apnea and acid reflux connection.
Call to Action:
Have you or someone you know experienced nighttime acid reflux? Share your experiences and tips in the comments below! Don’t forget to subscribe to ThePlantTube for more health insights and natural remedies.








