Ovarian cancer, though not as common as some other types, is a serious disease that affects women’s reproductive health.
Detecting the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer early and getting prompt treatment is crucial for better chances of survival.
Let’s dive into what ovarian cancer is, its risk factors, and the important signs to be aware of.
Read: Learn more about ovarian cancer.
Understanding Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. They make eggs and hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
The disease often goes unnoticed until it’s advanced, so catching it early is crucial for effective treatment.
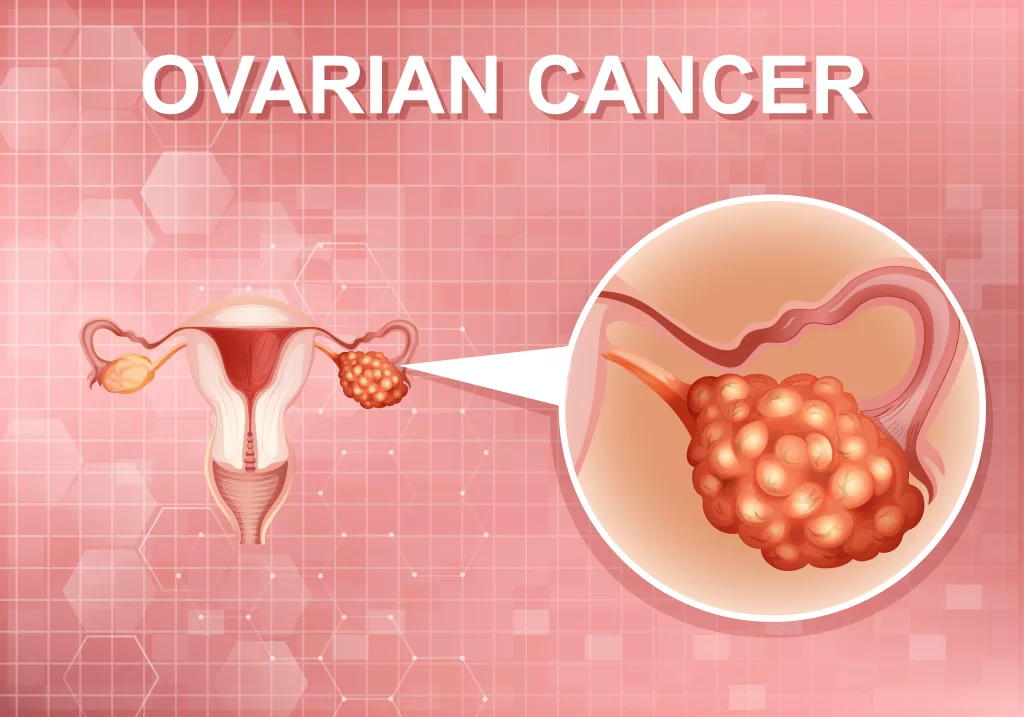
Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
While we’re not exactly sure why ovarian cancer happens, some factors increase the risk:
- Age: Women over 50, especially those over 65, are at a higher risk.
- Family History: If your family has a history of ovarian, breast, or colorectal cancer, your risk is higher.
- Inherited Mutations: Gene mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2 increase the risk.
- Personal History: Having had breast, uterine, or colorectal cancer slightly raises the risk.
- Endometriosis: When tissue lining the uterus grows outside it.
- Obesity: Being overweight may contribute to a higher risk.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Knowing the signs can improve your chances of early detection and successful treatment.
Read: Recognizing ovarian cancer symptoms
However, remember these symptoms can be vague and confused with other less serious conditions. If any persist for weeks and aren’t typical for you, consult a healthcare professional:
- Abdominal Discomfort: Persistent pain or discomfort in the abdomen or pelvis.
- Bloating: Unexplained bloating not improving with diet changes.
- Urinary Changes: Frequent urination or urgency, sometimes with difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Changes in Digestion: Persistent indigestion, constipation, or other gastrointestinal issues.
- Appetite Loss or Feeling Full Quickly: Sudden loss of appetite or feeling full even after small amounts of food.
- Fatigue: Unexplained and persistent fatigue, even after enough rest.
When To Seek Medical Attention
If you experience these symptoms often or notice a persistent unusual change in your body, consult a healthcare professional. While not necessarily ovarian cancer, they could indicate other health issues.
Read: When to see a doctor for ovarian cancer symptoms
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer is serious, but early detection can make a big difference. Knowing the risk factors and being aware of signs empowers women to protect their health.
Regular check-ups, talks with healthcare providers, and a healthy lifestyle are crucial for gynecological health.
Read: Tips for maintaining gynecological health
Remember, knowledge is power, and in the case of ovarian cancer, it can be life-saving.
Disclaimer: The following information is provided solely for informational purposes and should not be considered professional advice or a substitute for professional consultation. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information provided. Any reliance you place on such details is strictly at your own risk.