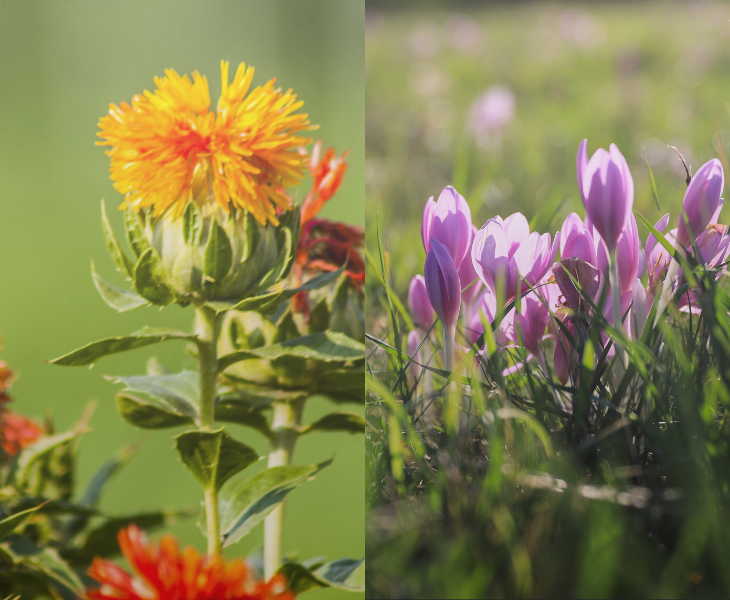
Safflower vs. Saffron – when it comes to spices renowned for their vibrant colors and unique flavors, safflower and saffron often steal the spotlight. Both are widely used in various cuisines and have a rich history dating back centuries.
However, they differ significantly in terms of health benefits, medicinal uses, and nutritional value.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the distinctive characteristics of safflower and saffron to help you understand their respective contributions to overall well-being.
Safflower: A Versatile Powerhouse
Health Benefits of Safflower

- Heart Health: Safflower oil, extracted from the seeds of the safflower plant, is a rich source of omega-6 fatty acids. These essential fatty acids have been linked to reduced cholesterol levels and a decreased risk of heart disease.
- Antioxidant Properties: Safflower contains compounds like flavonoids and phenolic acids that possess antioxidant properties. These antioxidants help combat free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which can contribute to chronic diseases and premature aging.
- Skin and Hair Health: Safflower oil is commonly used in skincare products due to its moisturizing properties. It helps maintain skin elasticity and hydration. Additionally, safflower oil may nourish the scalp, promoting healthier hair growth.
Medicinal Uses of Safflower
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Safflower has been traditionally used in herbal medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties. It may help alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and promote overall joint health.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Studies suggest that safflower extract may help regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Menstrual Health: Some traditional practices use safflower to ease menstrual discomfort and regulate menstrual cycles, although scientific evidence is limited in this regard.
Nutritional Value of Safflower
Safflower seeds are a good source of nutrients, including vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant, and several essential minerals like magnesium, potassium, and iron. However, it’s important to note that the majority of safflower products available in the market, such as safflower oil, are highly processed, which can affect their nutritional profile.
Saffron: The Golden Elixir
Health Benefits of Saffron

- Mood Enhancement: Saffron has been studied for its potential mood-enhancing effects. It may help alleviate symptoms of mild to moderate depression and anxiety. It is thought to work by boosting serotonin levels, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation.
- Eye Health: Saffron contains compounds, such as crocin and safranal, which have antioxidant properties and may help protect the retina from damage caused by oxidative stress. It has been associated with potential benefits for age-related macular degeneration and improving visual acuity.
- Digestive Aid: Saffron has traditionally been used to aid digestion and relieve gastrointestinal discomfort. It may help reduce symptoms of indigestion, bloating, and flatulence.
Medicinal Uses of Saffron
- Traditional Medicine: Saffron has a long history of use in traditional medicine, where it has been used for various purposes, including as an expectorant, sedative, and aphrodisiac. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before using saffron for medicinal purposes.
- Cancer Prevention: Preliminary studies suggest that saffron may have anticancer properties, inhibiting the growth of certain cancer cells. However, further research is needed to fully understand its potential in cancer prevention and treatment.
Nutritional Value of Saffron
Saffron is primarily used in small quantities as a spice, making its nutritional contribution negligible. However, it contains trace amounts of several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, manganese, and potassium.
Conclusion:
Safflower and saffron are two distinct spices with their own set of health benefits, medicinal uses, and nutritional value. Safflower oil, derived from safflower seeds, is rich in omega-6 fatty acids and possesses antioxidant properties. It may benefit heart health, skin, and hair.
On the other hand, saffron, known for its vibrant golden color, may have mood-enhancing effects, promote eye health, and aid digestion. Both safflower and saffron have long histories of use in traditional medicine, but it’s important to seek professional advice before using them medicinally.
Incorporating these spices into your culinary adventures can not only add delightful flavors but also potentially offer some health benefits along the way.
You can also visit our Facebook and YouTube pages to know more about plants and their health benefits.
You might also like:
- Vegetables With Highest Source of Omega-3: Omega-3 Rich Vegetables
- 5 Remarkable Benefits of Avocados For Gut Health
- Quality Sleep: Reducing Stress and Unlocking Other Remarkable Benefits
- 4 Great Positive Effects of Meditation To Our Bodies
- Understanding Stress: 6 Amazing Natural Remedies for Stress Relief